- Overview
- System requirements
- Install Scala
- Setting environment variables
- Download/clone windows utilities for corresponding Hadoop version
- Make /tmp/hive writable
- Run Spark shell
- Run PySpark
Overview
This is a quick tutorial how to install ApacheSpark on Windows via the pre-built on Apache Hadoop. It is assumed that the reader has basic knowledge of the Windows command line (CMD) and, if Bash should be used, a basic familiarity with Bash on Ubuntu on Windows (part of Linux Subsystem on Windows). We will demonstrate a basic example how to use Scala and Python (via PySpark) from the command line.
System requirements
We show how to install Spark on Windows 10 (see exact system info below) but generally it should also work on Windows 7. You will require (we give install instructions below)
- Windows 10 (prior versions, i.e. Windows >= 7, may work but not tested)
- Bash on Ubuntu on Windows (Linux subsystem on Windows) in case Bash should be used (not required per se)
- Java runtime environment (JRE) or Java Development Kit (JDK) version >= 8
- Scala
- Python (in case you want to use PySpark)
A general note of caution for Bash on Windows
If you plan to set up Bash on Windows to work with Spark etc. you will eventually edit configuration files of the Linux on Windows subsystem. It is very important that you do not use any Windows apps/tools to perform any operation on Linux files as these files may get corrupted. This includes using any Windows editor to edit Linux files (e.g. Notepad/++). For more details, see Do not change Linux files using Windows apps and tools.
Install Java
Binary installers for Java can be downloaded from Oracle Java SE. To run Spark, you only require a Java runtime environment (JRE) but you may also download the Java development kit (JDK) which includes the JRE. Note that the path to the JRE may be different when using a JDK.
You can check which version of Java you are running on the CMD via
java -version
In case you like to use Bash, you will need to install Java on the Linux subsystem for Windows separately as it is a distinct OS. You can do so by following instructions from @rs6g10 on Microsoft/BashOnWindows/Unable to install Java JDK or Runtime #49.
Install Python
If you like to use the Spark Python API via PySpark, you will need to install Python. A frequently recommended distribution is often that of Anaconda as it ships with a lot of useful libraries and has binary installers for Windows. Note that Bash on Windows already comes with Python 2.7 pre-installed so in case you like to work with Python3, you will have to install it using standard Bash workflow.
Example output for system
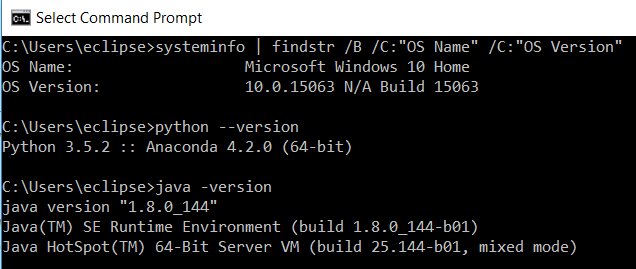
We show how our system is set up (your’s will probably vary). Type below commands in CMD (in succession)
systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"OS Name" /C:"OS Version"
java -version
python --version
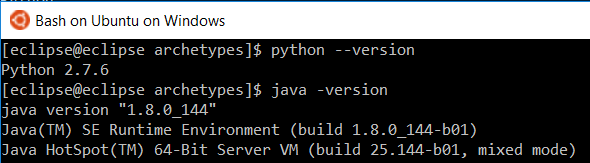
We can do the same for Bash (note the default version of Python)
Install Scala
Generally, you can find Scala downloads here. Find the Windows installer (in our case clicking on scala-2.12.3.msi under section Archive) downloads this. Follow installation wizard.
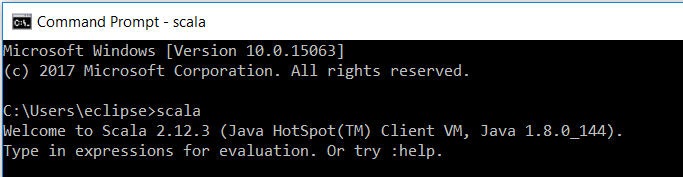
Once the installation is finished, open a new CMD and type
scala
Your output should look like this
Install Spark
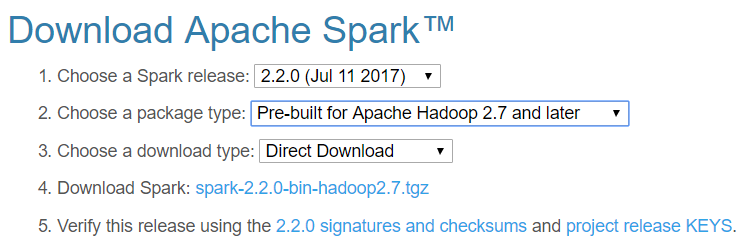
Find the latest stable version of Spark on Apache Spark Downloads and use pre-built on Hadoop and direct download.
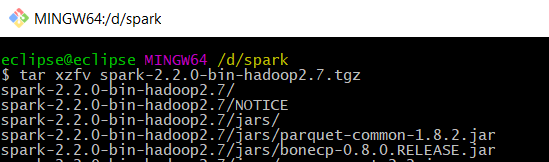
Copy/save the .tgz file to/at the location where you like Spark to reside and extract it from some Linux shell (e.g. Bash, Cygwin) via below command (your file name may vary). Alternatively, you can use some extraction software such as 7zip.
# in case tar program is not installed, install e.g. via sudo apt-get install tar
tar xzfv spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz
After some time, your Spark install (extraction) should be done and a couple of folders being created at your chosen location.
Setting environment variables
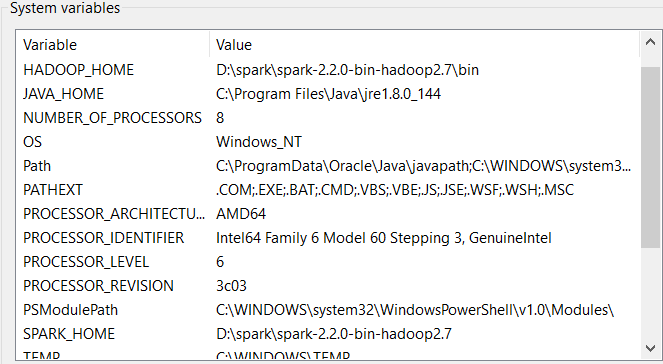
In order to make the system aware of all programs, we will be setting some environment variables. This can be done by simply using Windows search function in start menu and typing something like environment variables and clicking the program Edit the system environment variables. We will set the following variables (your location may vary)
- JAVA_HOME: C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_144
- SPARK_HOME: D:\spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7
- HADOOP_HOME: D:\spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7\bin
Moreover, we will expand the system path with
- C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_144\bin
- D:\spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7\bin
Note that the system environment variables are not necessarily shared with the Linux subsystem for Windows (although PATH seems to be shared). Any environment variable would thus have to be set in respective Linux configuration file.
Your Windows environment variables may look something like this now
Download/clone windows utilities for corresponding Hadoop version
Go to Github/steveloughran/winutils and clone/copy the Windows utilities for your Hadoop version to your local Hadoop directory. Copy \winutils-master\winutils-master\hadoop-2.7.1\bin and paste into your Spark install. For us this would be D:\spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7\bin.
Make /tmp/hive writable
To avoid a common error (see e.g. The root scratch dir: /tmp/hive on HDFS should be writable. Current permissions are: rw-rw-rw- (on Windows) or Apache Spark installation on Windows 10 open CMD as administrator and run below against your Spark directory where Winutils should reside (so in our case in D:\spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7\bin\bin)
D:\>spark\spark-2.2.0-bin-hadoop2.7\bin\bin\winutils.exe chmod 777 \tmp\hive
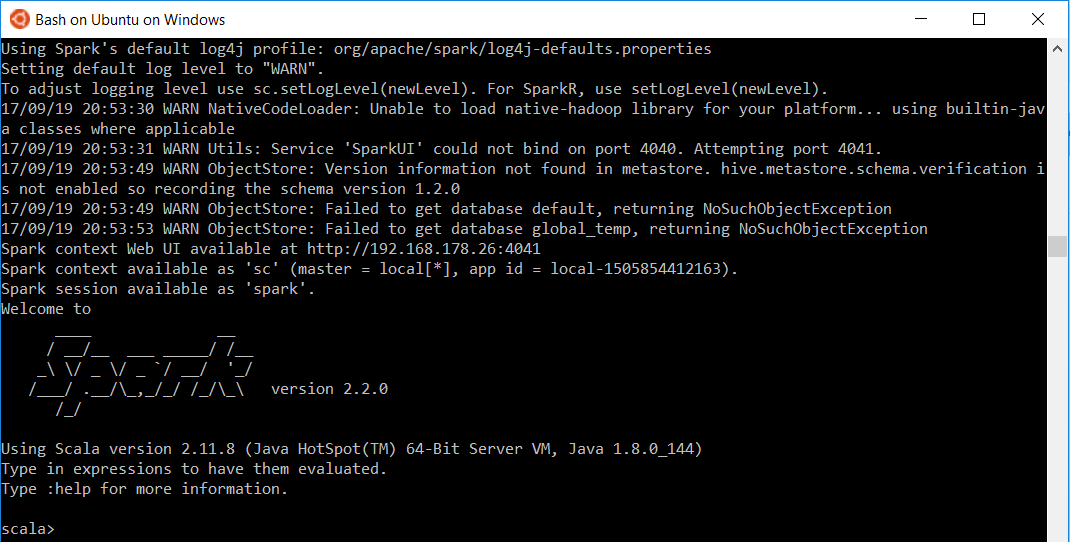
Run Spark shell
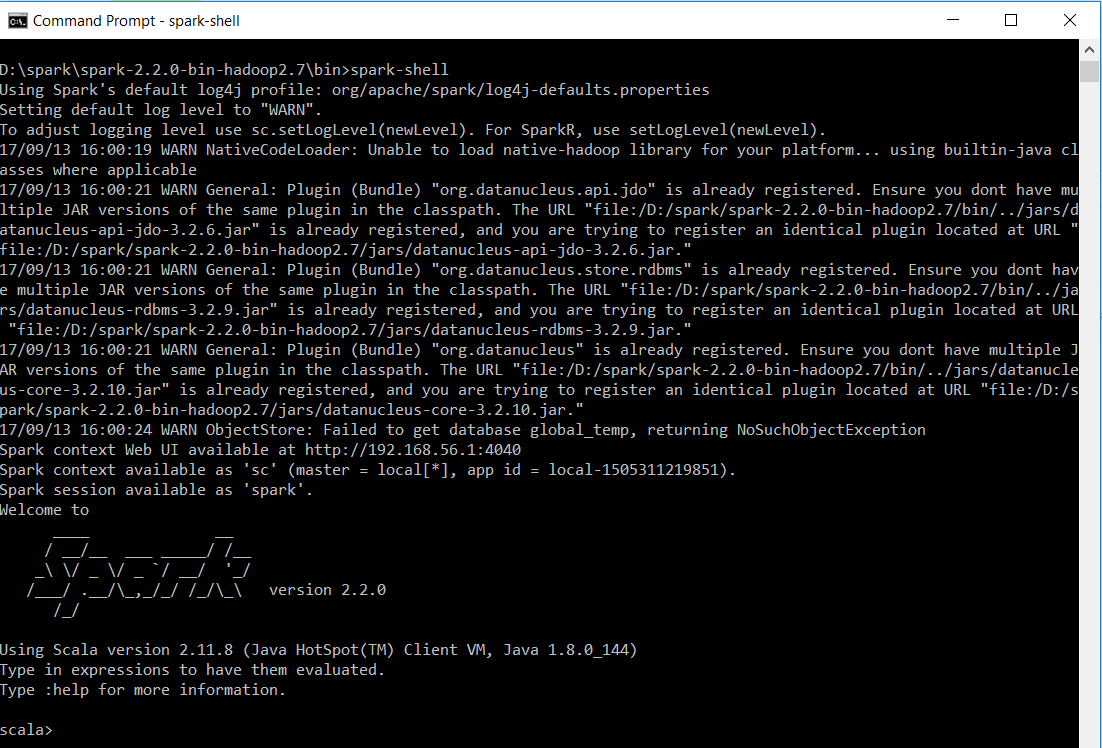
Finally, we can test our Spark installation by running the shell
spark-shell
Your output should look something like below
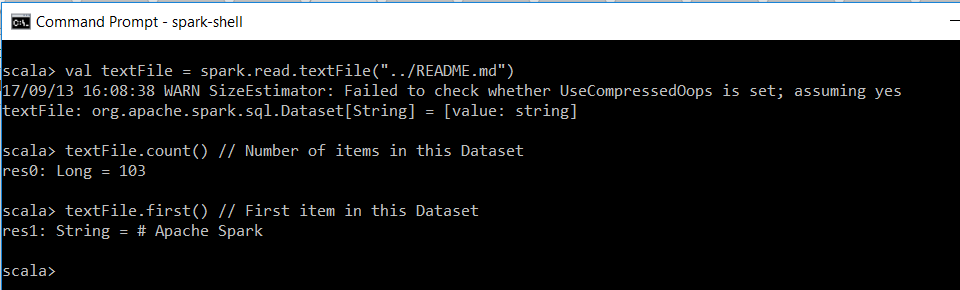
We execute a minimal example from Apache Spark Quick Start (note that the README file is located one directory up) to test basic functionality.
val textFile = spark.read.textFile("../README.md")
textFile.count() // Number of items in this Dataset
textFile.first() // First item in this Dataset
Since the Linux subsystem for Windows inherits the Path variables from Windows, we can run the same without further adjustments on Bash on Ubuntu on Windows
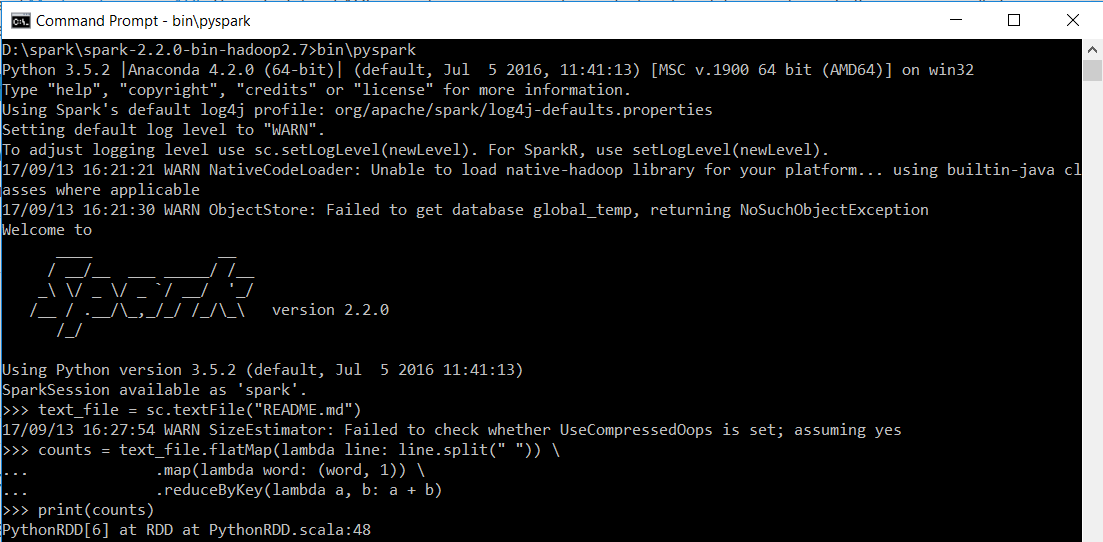
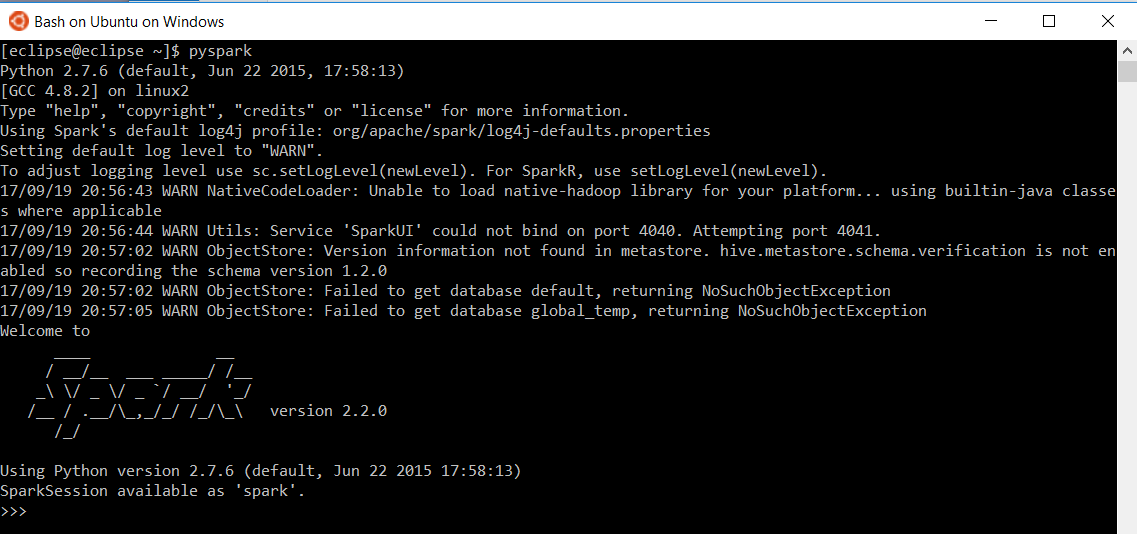
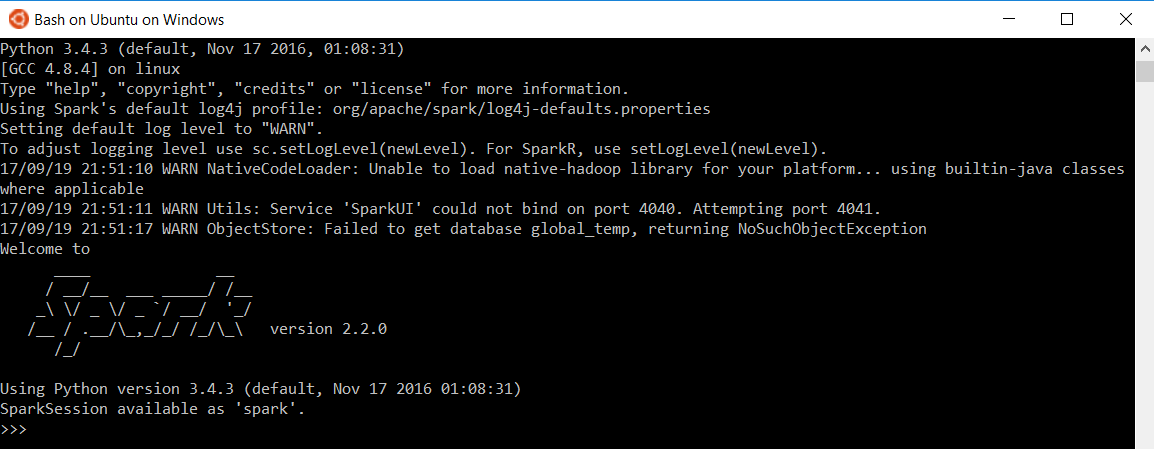
Run PySpark
Assuming you also want to use Python with Spark via PySpark and have followed above setup instructions, you can open a new CMD and type below to test if PySpark works
pyspark
# we show it with bin/pyspark but both will work if your environment variables are properly set
Again, we execute a minimal example from Apache Spark Examples.
text_file = sc.textFile("README.md")
counts = text_file.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" ")) \
.map(lambda word: (word, 1)) \
.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)
print(counts)
As before, the same command works in Bash but note the default Python version used
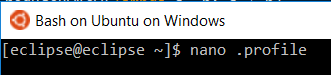
In case you want to work with a different Python version, adjust respective Bash configuration file to export the environment variable (see line below). In our case, we use Python3.4 and define it in the .profile file in the Bash home directory (~).
export PYSPARK_PYTHON=python3.4
The PySpark shell now runs Python 3.4 as default (this obviously needs to be adjusted in case you like to run a different Python version).